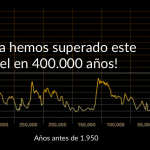
Los gases de efecto invernadero
- Paul l. Palmer. Título: The atmosphere, a very short introduction (2017). Editorial: Oxford University Press.
El cambio climático y la degradación de los ecosistemas marinos
- Viñas Rubio, J.M. (2013) El clima de la Tierra a lo largo de la Historia. Contenido en Clima, naturaleza y desastre. España e Hispanoamérica durante la Edad Moderna. Aberola, A. (coord.). Publicaciones de la Universidad de Valencia. pp: 225-229
- Abraham, J. (2017) What do jellyfish teach us about climate change? The Guardian. [en línea] Disponible en https://www.theguardian.com/environment/climate-consensus-97per-cent/2017/nov/03/what-do-jellyfish-teach-us-about-climate-change [consultado por última vez el 29 de enero de 2018]
- N.J., Mitchell; F.J., Janzen. (2010) Temperature-dependent sex determination and contemporary climate change. Sexual development. 2010, 4(1-2). pp: 129-140 | doi: 10.1159/000282494
- Fernández-chacón, A.; Bertolero, A.; Amengual, A.; Tavecchia, G.; Homar, V.; Oro, D. (2011) Spatial heterogeneity in the effects of climate change on the population dynamics of a Mediterranean tortoise. Global Change Biology. 2011; 17. pp: 3075-3088 | doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02469.x
- Jensen, M.P.; Allen, C.D.; Eguchi, T.; Bell, I.P.; Lacastella, E.L.; Hilton, W.A.; Hof, C.A.M.; Dutton, P.H. (2018) Environmental warming and feminization of one of the largest sea turtle populations in the world. Current Biology, 28. pp: 154-159 | doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.11.057
- Brenes, O. (2011) Efecto de la precipitación en el proceso de incubación de las nidadas de tortuga lora. Ambientales, 41. pp: 27-35
- Condon, R.H.; Duarte, C.M.; Pitt, K.A.; Robinson, K.L.; Lucas, C.H.; Sutherland, K.R.; Mianzan, H.W; …; Graham, W.M. (2013) Recurrent jellyfish blooms are a consequence of global oscillations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(3). pp: 1000-1005 | doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210920110
- Uye, S-i. (2008) Blooms of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Plankton & Benthos Research, 3. Pp:125-131. | doi: 10.3800/pbr.3.125
Nueva distribución microbiana
- McIntyre M, Setzkorn C, Hepworth P, Morand S, Morse A and Baylis M (2017) Systematic Assesment of the Climate Sensitivity of Important Human and Domestic Animals Pathogens in Europe. Nature 7.
- Bueno R and Jiménez R (2008) Malaria en España: Aspectos entomológicos y perspectivas de futuro. Scielo 82, 467-479.
Cuando escasee la hierba…
- E.S. Bakker, H. Olff & J.M. Gleichman (2009) Contrasting effects of large herbivore grazing on smaller herbivores. Basic and Applied Ecology, Volume 10,Pages 141-150, ISSN 1439-1791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2007.10.009. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1439179107001545
- Agencia Española de Consumo, Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (Aecosan) “Plan de Actuación sobre Tuberculosis en Especies Silvestres”. Ministerio De Agricultura Y Pesca, Alimentación Y Medio Ambiente. Disponible online: http://www.mapama.gob.es/es/ganaderia/temas/sanidad-animal-higiene-ganadera/patubes2017_3_tcm7-452413.pdf
- Soriguer Escofet, R. C. (2017) “TB en animales del Parque Nacional de Doñana”. En la Fundación de la Unidad de Investigación en Tuberculosis de Barcelona. Congreso Internacional de la UITB, Barcelona.
- Verdú, J.R., Cortez, V., Ortiz, A.J., González-Rodríguez, E., Martínez-Pinna, J., Lumaret, J.P., Lobo, J.M., Numa, C. & Sánchez-Piñero, F. 2015. Low doses of ivermectin cause sensory and locomotor disorders in dung beetles. Scientific Reports 5: 13912. DOI: 10.1038/srep13912.
- Maestre, F. T. & Soliveres, S. (2017) “Matorralización en tierras secas, una paradoja sin igual”. Investigación y Ciencia, Scilogs. Disponible online: https://www.investigacionyciencia.es/blogs/medicina-y-biologia/93/posts/matorralizacin-en-tierras-secas-una-paradoja-sin-igual-14980
- Mooallem, J. (2017) “El mundo ante la amnesia ambiental”. New York Times. Disponible online: https://www.nytimes.com/es/2017/04/24/el-mundo-ante-la-amnesia-ambiental-generacional/
- CSIC & Fundación BBVA “El clima de Doñana”. Cuadernos de Campo. Disponible online: http://www.cuadernosdecampo.es/Website/Climatologia/Default.aspx#Lluvia1
- Lumbierres, M.; Méndez, P. F.; Bustamante, J. & Santamaría, L. (2017) “Modeling Biomass Production in Seasonal Wetlands Using MODIS NDVI Land Surface Phenology”. Remote Sensing, 9(4), 392; doi:10.3390/rs9040392 http://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/9/4/392/htm
- Galiano, E. F. (1985) “Los riesgos del sobrepastoreo”. El Pais. Disponible online: https://elpais.com/diario/1985/02/03/agenda/476233205_850215.html
- Méndez, F.; Santamaría, P.; Amezaga, L.; Hearns, J. Glen. (2010) “Adaptive Strategies for Natural Resources and Ecosystems Management in Canada – Opportunities for Implementation in Europe”.
- Bustamante, J.; Santamaría, L.; Janss, G.; Green, A.; Beltrame, C.; Poulin, B.; Mihai Adamescu, C.; Cazacu, C. (2016) “Conserving dynamic wetlands under combined global, regional and local stressors”. EcoPotencial, European Union Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme. Disponible online: http://www.ecopotential-project.eu/site-studies/storylines.html?id=132
Infografía – Naturaleza vs Humanos
- Earth System Research Laboratory (2018) “Trends in Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide”. Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii. Disponible online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/
- World Health Organization (2017) “Climate change and health“. Disponible online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs266/en/
- Hunter, P. (2007). The impact of CO2. The global rise in the levels of CO2 is good for trees, bad for grasses and terrible for corals. EMBO Reports, 8(12), 1104–1106. http://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7401130
- NOAA. What is coral bleaching? National Ocean Service website, https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/coral_bleach.html, 10/10/17
- Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (2018) “GLEAM 2.0 – Evaluación de las emisiones de gases de efecto invernadero y su potencial de mitigación”. Disponible online: http://www.fao.org/gleam/results/es/
- World Wild Life. “Threats – Deforestation”. Disponible online: https://www.worldwildlife.org/threats/deforestation
- Riebeek, H. (2006) “Paleoclimatology: Explaining the evidence”. Nasa, Earth Observatory. Disponible online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/Paleoclimatology_Evidence/
Miles de años de historia bajo el hielo
- Doadrio, A.L. (2011). Cambio climático. Una visión global. Anales de la Real Academia Nacional de Farmacia, 77, 1-29.
- Fischer, D., Shirley, E., Whalen, C., Calamari, Z., Rountrey, A,.,… Lazarev, P. (2014). X-ray computed tomography of two mammoth calf mummies. Journal of Paleontology, 88 (4), 664-675.
- Oeggl, K., Kofler, W., Schmidl, A., Dickson, J., Egarter-Vigl, E., Gaber, O. (2007). The reconstruction of the last itinerary of Ötzi, the Neolithic Iceman, by polen analyses from sequentially sampled gut extracts. Quaternary Science Reviews, 26, 835-861.
- Rollo, F., Luciani, F., Marota , I., Olivieri, C., Luca, E. (2007). Persistence and decay of the intestinal microbiota’s DNA in glacier mummies from the Alps. Journal of Arcaheological. Science, 34, 1294-1305.
El museo en casa – Cambio climático
- Earth Science Communications Team. Global Climate Change. Vital Signs of the Planet. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. California Institute of Technology. https://climate.nasa.gov
El beso del monstruo
- Fernández-Lando, L. y Casellini, C.M. (2009). Ensayos clínicos de exenatida y su rol en el tratamiento de la diabetes tipo 2. Medicina, número 69, 447-457.
- Richard, J.E., Farkas, I., Anesten, F., Anderberg, R.H., Dickson, S.L., Gribble, F.M., Reimann, F., Jansson, J.O., Liposits, Z. y Skibicka, P. (2014). GLP-1 receptor stimulation of the Lateral Parabrachial Nucleus reduces food intake: Neuroanatomical, electrophysiological, and behavioral evidence. Endocrinology, 155(11), 4356-4367.
- Sierra-Ascencio, M.E., Ríos-Vaca, A. y Reza-Albarrán, A. (2006). Exenatide: uso en humanos. Gaceta Médica de México, 142(6), 483-491.
- Xie, J., El Sayed, N. M., Qi, C., Zhao, X., Moore, C.E. y Herbert, T.P. (2014). Exendin-4 stimulates islet cell replication via the IGF1 receptor activation of mTORC1/S6K1. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, número 53, 105-115.
Estrategias geopolíticas chinas frente al Cambio Climático
- P.D.A. Kraaijenbrink (2017). ‘’Impact of a global temperature rise of 1.5 degrees Celsius on Asia’s glaciers’’. Nature.
- B. Casassus (2014) ’’China predicted to outspend the US on science by 2020’’ Nature.
- C. He, L. Yang (2011). ‘’Desarrollo urbano y cambio climático en el delta del río Perla de China’’ Lincoln Intitute.
- G. C. Nelson, M. W. Rosegrant, J. Koo, R. Robertson, T. Sulser, T. Zhu, C. Ringler, S. Msangi, A. Palazzo, M. Batka, M. Magalhaes, R. Valmonte-Santos, M. Ewing, D. Lee (2009) ‘’Cambio Climático: El impacto en la agricultura y los costos de adaptación’’. Instituto Internacional de Investigación sobre políticas alimentarias.
- V. Shiva (2004) ‘’La guerra del agua: contaminación, privatización y negocio’’. Icaria.
- M. T. Rodríguez-Rodríguez (2010) ‘’Autosuficiencia alimentaria en China’’. Instituto de Investigaciones económicas de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.
- Fondo Monetario Internacional(2015) ‘’Boletín 2015’’
- J. Albert-Ferrero (2015) ‘’La China actual. Geoestrategia en su entorno geopolitico’’ Instituto Español de Estudios Estratégicos.
- J. González (2017) ‘’RCEP, el gran acuerdo comercial de China, India y Japón’’ Global Politics and law.
- K. Bradsher (2017) ’’A pesar de sus promesas para combatir el cambio climático, China busca extraer más carbón’’ The New York Times.
- Banco Mundial (2016) ‘’Datos Población Urbana’’
- E. Gómez Pérez-Cuadrado (2016) ‘’Plan Made in China 2025’’ Embajada de España en Pekín
- C. Müller-Markus (2017) ‘’El cambio climático: Un cuento chino con final feliz’’ CIDOB.
- L. Meyer( 2017) ’’El calentamiento global inflama la geopolítica’’ Ethic.
- R. Cervera, M. Carreras-Solanas, M. J. Masnou, Y. González, C. Canals (2017) ‘’Luces y Sombras De La Expansión Urbana China’’ Barcelona-shanghai Women Bridge.
- Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (2016) ‘’La seguridad alimentaria futura del mundo peligra debido a múltiples desafíos’’
- Banco mundial (2017) ‘’Rentas del petróleo’’
- Instituto de Estrategia. (2017)’’La geopolítica de la energía en el Ártico: recursos y rutas’’
- A. Riu (2014) ‘’El boom energético del Mar Caspio’’ El Orden Mundial.
- F. Arancón(2016) ‘’El TPP: un pulso geoeconómico sobrevuela Asia-Pacífico’’ El Orden Mundial.
- Sputnik Mundo(2017) ‘’China se posiciona como lider mundial de las energías renovables’’
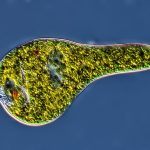
La euglena y su temor por la luz azul
- Iseki, M., Matsunaga, S., Murakami, A., Ohno, K., Shiga, K., Yoshida, K., Sugai, M., Takahashi, T., Hori, T. and Watanabe, M. (2002). A blue-light-activated adenylyl cyclase mediates photoavoidance in Euglena gracilis. Nature, 415(6875), pp.1047-1051.
- Ozasa, K., Won, J., Song, S., Tamaki, S., Ishikawa, T. and Maeda, M. (2017). Temporal change of photophobic step-up responses of Euglena gracilis investigated through motion analysis. PLOS ONE, 12(2), p.e0172813.
- Gibbs, S. (1978). The chloroplasts of Euglena may have evolved from symbiotic green algae. Canadian Journal of Botany, 56(22), pp.2883-2889.
Las esponjas marinas: biología, importancia y sorpresas
- HICKMAN, C. P.; ROBERTS, L. L.; KEEN, S.L.; LARSON, A.; L’ANSON, H.; EISENHOUR, D.J. (2009). Principios integrales de Zoología. Editorial McGraw-Hill. 14ª edición.
- LEE, W.L.; REISWIG, H.M.; AUSTIN, W.C., LUNDSTEN, L. (2012) An extraordinary new carnivorous sponge, Chondrocladia lyra, in the new subgenus Symmetocladia (Demospongiae, Cladorhizidae) from off of northern California, USA. Invertebrate Biology. December. Volume 131, issue 4, pp: 259-284 | doi: 10.1111/ivb.12001
- MALOOF, A.C.; ROSE, C.V.; BEACH, R.; SAMUELS, B.M.; CALMET, C.C.; ERWIN, D.H.; POIRIER, G.R.; YAO, N.; SIMONS, F.J. (2010) Possible animal-body fossils in pre-Marinoan limestones from South Australia. Nature Geoscience. Nº 3. pp: 653-659 | doi:10.1038/ngeo934
- MORA CRISTANCHO, J.A.; UMBREIT, F.N.; SANTOS-ACEVEDO, M.; NIEVES, J.S. (2008) Evaluación de extractos de esponjas marinas como nuevas fuentes de sustancias antimicrobianas. Revista Española de Quimioterapia. Nº 21. Vol. 3. pp: 174-179 | id: ibc-77588
- RIESGO, A.; FARRAR, N.; WINDSOR, P.J., GIRIBET, G.; LEYS, S.P. (2014) The analysis of eight transcriptomes from all Porifera classes reveals surprising genetic complexity in sponges. Molecular biology and Evolution. Nº 31. pp: 1102-1120 | doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/
- SAGAR, S.; KAUR, M.; MINNEMAN, K.P. (2010) Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges. Marine drugs. Nº8, Vol. 10. pp: 2619-2638 | doi: 10.3390/md8102619
- AIZENBERG, J.; SUNDAR, V.C.; YABLON, A.D.; WEAVER, J.C.; CHEN, G. (2004) Biological glass fibers: correlation between optical and structural properties. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Nº101, Vol. 10. pp: 3358-3363 | doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307843101
- SCHILL, R.O.; PFANNKUCHEN, M.; FRITZ, G.; KÖHLER, H-R.; BRÜMMER, F. (2006) Quiescent gemules of the freshwather sponge, Spongilla lacustris (Linnaeus, 1759), contain remarkably high levels of Hsp70 stress protein and hsp70 stress gene mRNA. Journal of Experimental Zoology, Volumen 305A. pp: 449–457 | doi: 10.1002/jez.a.281
- WARN, F.; PONTES, M (trad.) (2018) Esponjas: ¿El oro de Kalymnos? Marenostrum [en línea] Recuperado de http://marenostrum.org/bibliotecadelmar/historia/esponjas/
Los murciélagos: entre sombras y ecos
- CURTIS, ; SCHNEK, A.; BARNES, N.S.; MASSARINI, A. (2008) Biología. 7ª edición. Editorial Médica Panamericana.
- DELIBES, ; PALOMO, J. (2007) Atlas de los mamíferos terrestres de España. Ministerio de Agricultura, alimentación y medioambiente. Gobierno de España.
- DE PAZ, ; BENZAL, J.; FERNÁNDEZ, R. (1990) Criterios de valoración de refugios para murciélagos: aplicación al inventario nacional. Ecología, 4. pp: 191-206.
- ÁLVAREZ, ; RIAL, S.; CERQUEIRA, F.; SEAGE, R.; ARZÚA, M.; LAMAS, F.J.; HERMIDA, R. Importancia das minas de galería na conservación de morcegos de Galicia. Minaría e xestión ambiental.
- SOSA, V.; HERNÁNDEZ-SALAZAR, E.; HERNÁNDEZ-CONRIQUE, D.; CASTROLUNA, A.A. (2008) Murciélagos. Capítulo incluido en MANSON, R.H.; HERNÁNDEZ-ORTIZ, V.; GALLINA, S.; MEHLTRETER, K. (eds.) (2008) Agroecosistemas cafetaleros de Veracruz: biodiversidad, manejo y conservación. Instituto de Ecología A.C. (INECOL) e Instituto Nacional de Ecología (INE-SEMARNAT)
- ARITA, T., WILSON, E. “Long-Nosed Bats and Agaves: The Tequila Connection” BATS magazine. 5(4) [en línea]
- BAT CONSERVATION INTERNATIONAL. Frequently asked questions about bats.
- LISÓN, ; ALEDO, E.; CALVO, J.F. (2011) Los murciélagos (Mammalia: Chiroptera) de la Región de Murcia (SE España): distribución y estado de conservación. Anales de Biología , 33. pp: 79-92
- FERNÁNDEZ, Z.; TABLANTE, A.; BARTOLI, F.; BEGUIN, S.; HEMKER, H.C.; APITZ-CASTRO, R. (1998) Expression of biological activity of draculin, the anticoagulant factor from vampire bat saliva, is strictly dependent on the appropiate glucosilation of the native molecule. Biochimica et Biophysica acta; 1425(2). pp: 291-299
- TAMSITT, J.R.; VALDIVIESO, D. (1970) Los murciélagos y la salud pública. Boletín de la Oficina Sanitaria Panamericana. pp: 122-140
Plantas extraterrestres
- Paul, Anna-Lisa et al. “Plant Growth Strategies Are Remodeled By Spaceflight.” BMC PLANT BIOLOGY, vol 12: 1, 2012, pág. 232. Springer Nature, doi:10.1186/1471-2229-12-232.
- Herridge, Linda, and Amanda Griffin. “How Does Your Space Garden Grow?.” NASA, 2017, https://www.nasa.gov/feature/how-does-your-space-garden-grow
- Meggs, Lori. “NASA – Growing Plants And Vegetables In A Space Garden.” Nasa.Gov, 2017, https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/station/research/10-074.html
- Herridge, Linda. “Veggie Activated To Grow Fresh Plants On Space Station.” NASA, 2017, https://www.nasa.gov/content/veggie-plant-growth-system-activated-on-international-space-station
¿Qué coches emiten más gases de efecto invernadero?
- Vlachokostas, Ch., Nastis, SA, Achillas, Ch. et al. 2010. Economic damages of ozone air pollution to crops using combined air quality and GIS modelling. Atmospheric Environment. 44:3352-3361. Cars and CO2. Transport & Environment
- Straif, Kurt, Cohen, Aaron, Famet, Jonathan (eds.). 2013: Air Pollution and Cancer. IARC Scientific Publication No. 161.
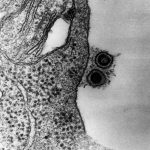
Tupanvirus, virus en la frontera de lo vivo
- Abrahão, J., Silva, L., Silva, L. S., Khalil, J. Y. B., Rodrigues, R., Arantes, T., et al. (2018). Tailed giant tupanvirus possesses the most complete translational apparatus of the known virosphere. Nature Communications, 9(1), 749.
- Philippe, N., Legendre, M., Doutre, G., Coute, Y., Poirot, O., Lescot, M., et al. (2013). Pandoraviruses: Amoeba viruses with genomes up to 2.5 mb reaching that of parasitic eukaryotes. Science (New York, N.Y.), 341(6143), 281-286.
- Shors, T. (2009). Virus: Estudio molecular con orientación clínica. Chapters 1 and 2. Ed. Médica Panamericana.